Introduction to Computers Using Ubuntu
Glossary
While you may prefer to read the main sections of this guide to learn about each of these terms in the context presented there, the glossary may provide you valuable, quick access to the terms.
Please suggest additions!
This glossary may lag behind the development of the other guide sections. Please be patient.
When it seems appropriate, for unusual terms inside a glossary entry, there are links to external sites. Often the initial site is Wikipedia. Wikipedia is a modern encyclopedia entirely on the Web. It has an extra dimension when compared to other traditional encyclopedias. Wikipedia is edited by thousands of individuals, with the entries checked and rechecked as new information becomes available. Unlike the paper encyclpedias of my own youth which had an annual update volume, Wikipedia is frequently updated within minutes of the appearance of new information.
Even professional educators are beginning to accept Wikipedia as a new-format encyclopedia, seeing it as a starting point for student research. Even then, you should always do a wide search for answers. Just because an item is the top link on a Google search does NOT make it the definitive answer. Just because a statement appears on a Wikipedia entry does not make it authoritative. Wikipedia, like any other encyclopedia, is simply one place to start.
- accessibility
- Ubuntu has tools like a screen reader available among other tools to compensate for users with reduced vision. There's also a zoom feature to selectively enlarge the screen image. These features are not turned on by default. Look for a list of these features in the System Settings.
- affiliate
- One way that websites make money is through ads placed on the site's pages. These ads often link directly to an online store such as Amazon. The website owner gets a payment for anything that is purchased by the person who follows the ad link to the online store.
- ASCII
- ASCII is an abbreviation for "American Standard for Computer Information Interchange" which allows 8-bit codes to represent every digit, letter, punctuation mark and some special characters. It was obvious very early on that everyone needed to conform to a coding standard so the data from one company's data tape would read into another company's machine representing the same data. ASCII codes remain valid, but are now part of a larger coding system, the UTF (Unicode Transformation Format) which allows not only the standard alphabet, but letters with accents, and all known alternate alphabets like Arabic (سلام - "peace"), Chinese (和平 - "peace"), Cyrillic (мир - "peace") Hebrew ( שָׁלוֹם - "peace"), Hindi (शांति - "peace") in addition to the pictorial "emoji" ☺ which are also known as "smileys." The Web pages of this computer guide are coded using the most common UTF code version known as UTF-8 so all sorts of languages can be included and displayed properly not only the English which ASCII supplies in the first 128 codes of the UTF system.
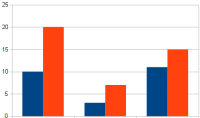
- bar chart
- When you need to make comparisons between two sets of numbers, a bar chart is the best choice. LibreOffice Calc calls the tall bars "column charts" instead, but both show the same information, with only the orientation of the comparative bars being different.
- binary
- Binary means simply "two states" like on or off. Computers, because they are filled with switches, are a natural for using information coded into binary formats. A single switch can mean just two things "on" or "off" or "one" or "zero". Coding in binary uses groups of switches to carry information. The most well known group is a group of 8 switches, a "byte". Coding in binary is therefore, usually represented as a set of eight digits: 00001111 which carries a meaning very different from 11110000 or 10101010. [ Read More at Wikipedia ]
- boot
- The hardware of a computer is all switches and needs settings for those switches. At the instant of startup, it must "pull itself up by its bootstraps." That's an old saying to describe a complete start from scratch and today we say "boot" when we mean, "Start up my computer. Get the set of operating instructions to set my switches and get to work." The first instructions are a general operating system like Linux or Windows or MacOS. Then we personally start our choice of application like a word processor. Today's phones (smartphones) don't often get turned entirely off. That means that they are ready to go at the tap of a button or a tap of their screen. Sometimes we need to force a full reboot (restart from scratch) by opening the phone, removing-and-replacing the battery for a "cold" boot, a boot from zero electric voltage available.
- broadband
- The speed of an Internet connection is measured by how many bits of information are transferred per second. Earlier phone line connections (called "dial-up") were relatively slow at 56 kilobits (56,000 bits) per second. Anything beyond that speed has been called broadband or "high-speed" Internet. A typical house connection is better than 10,000,000 (ten megabits) per second. People will use several terms for broadband, including "DSL", "Broadband Cable", and "FiOS" among others. The choices for broadband in your area depend on the companies which have run the wires on the utility poles.
- button
- The GUI of modern computers present small icon graphics to represent tasks you can start. To start the task, you left-click the button or icon.
click A person starts actions or selects “objects” on the computer by a quick push-and-release of one of the buttons at the finger end of the mouse. See also: point-and-click, left-click, right-click
- CamelCase
- When trying to avoid using spaces in file names, and in naming program variables, etc., one common convention is to capitalize the first letter of each word so they stand out as the start of a new word in the FileName. Other conventions used to avoid spaces in file names include dashes, file-name or underscores, file_name.
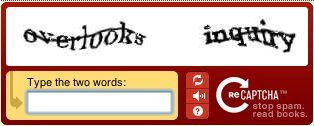
- CAPTCHA
- This acronym represents "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart" and is used to try to make it difficult for automated "bot" software to seem human. It is commonly used to prevent the automated software from setting up accounts on email services, social networks, etc. You are asked to enter text which has been skewed and colored in such a way to make computerized scanning and interpretation difficult or impossible. For the example shown here, you would type the two words "overlooks" and "inquiry" into the space indicated. If you cannot recognize the words yourself, you may click the top of three buttons
 to generate a new word pair. Official CAPTCHA Site
to generate a new word pair. Official CAPTCHA Site
Some, more recent versions of captcha ask you to identify things found only in some of a set of photos, such as pictures with cars in them.
(There are many people who object to the captcha system altogether because it is often used to "check in" at Google reCAPTCHA in a privacy-invading way, "tracking" your visits to a web site, or, in the case of the photo identification versions, to help train artificial intelligence tools to "see" objects in those photographs.)
- cell
- The grid of a spreadsheet is divided into small elements called cells which can contain three kinds of information: values, labels and formulas. You don't move a cursor around the screen, really. You jump from cell to cell instead.
- cloud
- As a feature of the current Internet, it is possible to work with programs and storage that are running as a service through a small software client on the computer on your desk or your lap. The "cloud" is a marketing term, too. It stongly suggests that your data is "somewhere out there". Google is well known for providing "Google Drive" which provides the basics of word processing, spreadsheets, and presentation software with files automatically stored on a distant hard drive, NOT on your own computer. The biggest benefit is accessibility. You can easily work on the file from several computers and even simply share your files with others. The file is just another Web address you access with your browser. Google, Mozilla, Microsoft and several other companies are working on making the cloud replace a standard computer. Google sells the Chromebook which is specifically designed to work with cloud tools. The entire Chromebook philosophy is a Web-based one. All computer features are dependent on being
connected to the Internet. It is exactly like the smartphone in that way. A cell phone isn't really much use if you cannot connect, "no bars", as they say.
- command
- Typing an instruction that the computer should follow is a “command.” There is a non-GUI “command line” method to direct a computer's action. People who program computers or who want to set advanced features of their computers often go “behind” the graphical user interface to do their work.
- computer
- General purpose information processing tool.
- context menu
- Using the right mouse button to point-and-click will typically give you a small box which lists options that apply to the screen/object at which your pointer is pointing.
- cursor
- It is a marker to show the current location in a word processing document. The next letter you type will be inserted at the location of the cursor. The cursor is usually represented by a vertical flashing line, though you may also see it as a flashing line along the bottom edge of the text line.
- CPU - Computer Processing Unit
- Sometimes called the "brain" of the computer, the CPU is more accurately understood as the part in which programming instructions act on data passing through our digital devices. CPU chips are the main hardware component of a computer, no matter what brand. Common CPU manufacturers are Intel, AMD and ARM. Intel is credited with the development of the X86 architecture which is the one most used in modern desktops and laptops. X86 CPUs are complex and need a fair amount of power to do their work. Cellphones have to use far less power in order to be able to fit into a purse or pocket. Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) is the most well known manufacturer of such power-sipping CPUs. One reason that GNU/Linux is well regarded is that it has been "ported" to work on almost every CPU architecture that exists.
- default
- Most computers allow you to set features to your own preference, but there are also default behaviors for every action. In general, the default behaviors are set so that you do the same things for the same results no matter what application you are using. A default behavior makes everyone's life easier.
- distribution
- Free Software is easier to get than it used to be, thanks to the Internet. There are several companies and community groups organized around making Free Software even easier to install and use. Ubuntu is a distribution of a selected set of Free Software. The distribution is a preliminary selection from the thousands of available programs. The distribution gives you a “running start” by providing an operating system, a music player, a word processor, a photo manipulation tool, etc. There are many distributions. Ubuntu is just one of them. Check out Mint, Debian, Fedora, OpenSUSE as other examples.
- dialog
- Frequently, when you choose an option within a program, a small window pops up on the screen within the larger program window. Within that smaller window, you can enter details or make further selections to complete applying the option features. Sometimes you will hear the "dialog" term expressed as "dialog box" or "wizard" or "popup window."
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- The domain name system of the Internet translates addresses from human-readable words into machine-readable number codes, one each for the addresses of computers on the world-spanning network.
- encrypt
- As a part of strong security measures, you may decide to recode a file so only you can restore it. You give a “key” that is like a password that must then be entered again to access the protected file. The most common encrypted files are your user name and password that you type to connect to online banking. The encrypted information cannot be decoded without the key. Your browser sets up the encryption key automatically with the bank, in this case.
- double-click
- Tapping the left mouse button "usually" just highlights an item. To launch a program or activate an application typically requires you to double-click the left mouse button. You must click quickly. The actual delay can be set in the system settings. Ubuntu does not require double-click for icons in some situations. A single click will launch an application in the system tray, for example. Macintosh users may balk at the double-click, since the Macintosh operating system uses a single click for the launch action.
- field
- Data is collected in database files or spreadsheet cells. All the cells in a single column need to contain the same kind of information, either first name or last name so that all first names are in the same column. A single row of cells is called a record which contains all the field data for an individual.
- file
- This is the generic term for any document as it is stored on a computer's hard drive or a removable drive like a USB thumb drive. File types are often identified by their extensions. JPG is the extension for a photo file, for example. The extension for a word processing file is ODT if it is stored in the Open Document Format used by programs like LibreOffice.
- flash drive
- A removable solid state storage device. Usually small, about the size of a thumb which makes it often called a "thumb drive." In 2013, a 4GB flash drive is the smallest size sold and prices range downward from $15 for that size, depending on the brand. Sizes up to 128GB are commonly available. Flash drives are mainly used as removable storage and plug into one of the USB sockets on a computer. The term "flash" is both a reference to the speed of the drive and the electronic technology that makes the storage persistent, not needing a supply of electricity to maintain the state of the storage.
- folder
- Although the files are electronically stored, it is convenient to organize those files in a way that mimics the way we would physically store paper documents. On a computer, we put a document file into a virtual manilla folder and digitally store it in a file cabinet. Using folders organizes things mentally, too. A computer's digital hard drive, even a removable USB solid-state drive, benefits from organization. Creating sensible electronic folders ahead of time, before saving your work, makes it easier to find individual files later.
- Graphic Processing Unit (GPU)
- Processing the instructions for images, especially high-speed animations in games or smooth renderings of movies require a lot of computer power. Way back in the development of screen-oriented computing, it was recognized that the graphics instructions deserved special treatment, a dedicated processor, just for graphics. Very efficient chips do the job. In most cases, there's an integrated GPU, but hard core game players will want dedicated graphics support and buy expensive graphics cards to add to their computer. The software for these cards has been contentious for years. Each manufacturer has "driver" software which is proprietary. GNU/Linux users typically have to agree to install binary blobs (AKA "third party software") for best graphic performance. Open Source driver software is being concurrently developed, but because it is being reverse engineered to avoid copyright and patent issues, may be less efficient than the driver from the card's manufacturer.
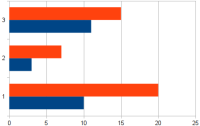
- Line Graph
- To show a series of measurements which change as time passes, a line graph or line chart is best.
- GNU/Linux
- Every computer has an operating system, the base software that lets users add tools like word processors and deals with printing, saving, etc. GNU is the broad term for the system control tools that surround a central core or “kernel” that is called Linux. It is common to hear people refer to this operating system as “Linux” in the same way that people say “Windows” instead of “Microsoft Windows XP” or “Microsoft Windows 7.”
- GUI
- (also Graphical User Interface) is the system of using a mouse to manipulate the program while doing a task on the computer. Pointing and clicking on icons or copying and pasting with visual cues are a big part of a GUI.
- hover
- Especially on Web pages, simply moving the mouse pointer to an icon will reveal a hint. Hovering over the toolbar buttons (icons) of most programs also reveals the purpose of the tool that the icon represents. (See also: tool tip)
- hard drive
-
- Your computer needs a place to store data so it isn't lost when the electricity to your computer goes off. Most computers have a magnetic device with disks that spin and on which data is recorded. The hard drive is typically found inside the tower box of your home computer or might be as smaller version tucked under the keyboard of your laptop. See SSD below, too.
- hot keys (Keyboard Shortcuts)
- There are "special" key combinations which perform common tasks. Ctrl+C (holding down the control key while tapping the C key is a consistent shortcut for copying selected/highlighted text, images, files into the computer's clipboard. Similarly, Ctrl+V is the shortcut for "pasting" the clipboard contents into a new file (or folder, as appropriate). This guide has a Common Keyboard Shortcuts page.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
- A system of marking information to deliver it to you computer so that it is visually appealing with a mixture of text sizes and styles along with media elements like photographs, sound and video. The system was proposed by Tim Berners-Lee in the early 1990s. Because it solved many problems, HTML made the World Wide Web take over the majority of information exchanged on the Internet wiring. The software that displays Web pages is called a "browser."
- icon
- Part of the Graphical User Interface (GUI) is using small images to represent important capabilities of the program you are using. The toolbars of most programs have icons for printing, for example. An icon might be intended to look like a printer. Look closely. Of course, it may not actually look like your own printer. Icons are usually small so many of them fit on a toolbar.
- input
- Computers need information to do their work. People use devices connected to the "box" to supply that information. The keyboard and mouse are the two most common input devices, but touchpads, touch screens, cameras and microphones also qualify as input devices.
- ISP (Internet Service Provider)
- A company that provides all the networking services associated with an Internet connection. The services typically include a home router, email, and technical support for Internet problems. Typically, people purchase the service from the same company which provides cable television or phone service. Sometimes the ISP will also provide Web page creation options.
- keyboard
- Traditional computer input device which has the basic look of a typewriter with the letters/numbers, but with additional keys that make working with a computer easier.
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- Within your house, all the computers are connected to a router for access to the Internet. In addition, you can make easy links between them to share access to printers, share files, movies and music. The LAN shares an address set that make connecting easy.
- left-click
- The left hand button of a mouse is the selection/action button. Typically a single click of the left button selects (highlights) something. A double-click on an icon launches or activates a program.
- legend
- In graphs (or "charts" as LibreOffice calls them), the data points are often identified by colored markers or with different symbols for each set of data in the chart. A well made chart identifies these colors or marks with a list called a legend which is located to the right of the chart itself.
- link
- Connecting from page to page on the World Wide Web is accomplished with the use of links, usually a link is blue text that is also underlined in blue. Each term on this page has a link from one or more of the pages in this guide. They are also called hyperlinks and have a history from before the World Wide Web, but the Web is the place where hyperlinks have blossomed into their current value.
- monitor
- The screen which displays your view of the Internet or any other output from the computer is called many terms. CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) was one of the earliest while computers were still exclusively a very techie thing. Monitor was next and remains a mostly techie term, too. Most users these days think of it as a "screen", reflecting the connection with the even more familiar TV screen. In fact, many of the flatscreen television screens can be directly connected to a computer. Instead of looking at a 14 inch diagonal monitor on your laptop, you can connect the computer to the huge screen in your living room and watch a movie.
- mouse
- Hand-held input device to point at and select from options visible on the computer's screen.
- multi-task
- Modern CPUs are able to do parallel processing of instructions because they have more than one core. Each core can be focused on doing the instructions for a single process/program while other programs run simultaneously on other cores. That reduces the need for one monolithic core to share its resources on multiple programs. The end result is that you can be listening to high quality music from your computer while writing your novel in a word processor, and your email is updating with new messages as needed.
- muscle memory
- Muscle memory is what happens when you do things over and over. Touch typing on a keyboard is a perfect example of muscle memory. When you first learn to type, you must think about where to move a particular finger in order to type a letter. Gradually, you develop a habit about the most common letters and eventually, the habits develop so well that you do not need to consciously think about the action of typing a whole paragraph. The individual fingers just seem to "know" what to do all on their own.
- Natick Community-Senior Center
- Natick, Massachusetts, a community west of Boston, is the 'home' of the NatickFOSS User Group. Meetings are held at the recently completed community and senior center where classrooms with digital projectors make it easy for members to share their expertise with everyone.
- output
- After processing information, the computer produces a visible or audible result. That output may be displayed on a monitor, printed to paper, or viewed as a video or audio product.
- password
- Security of files and access to online accounts requires a password that only you know, but also that you can remember.
- phishing
- If you get an email warning that your credit card may have been compromised with a charge made by somebody else, but then you are asked to click a link so you can "log in to fix the problem", that's "phishing". Don't do it. The email link will NOT take you to the credit card site. It will probably just go to a scammer's site where you'll carelessly type both your user name and password into a couple of blanks...unwittingly giving the login credentials to the crook who owns the site. Be alert, don't be rushed! Think before you click an email link.
- pointer
- The mouse controls an image (typically an arrow) which moves around the computer's screen while the human hand moves the mouse.
- point-and-click
- You will select and activate events with a quick push-and-release of the mouse button while the pointer is hovering over something visible on the screen.
- proprietary
- When a single company or corporation holds the exclusive rights to distribute and modify a product, then it is "proprietary." FOSS software is the opposite of proprietary software. Anyone has the permission to improve and redistribute the software. Free Software removes most limitations. The only restriction is that someone is not allowed to take FOSS and make it proprietary.
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- The "action" of apps and programs happens at a rapid pace so you can get your work done with limited delay. Making that possible is the thousands of electronic switches which store the app instruction codes and the data so they can work together to let you write a story, play your favorite song, edit a video or anything else. Electronic switches turn on and off so quickly that you don't sense the delay during the process you are doing. RAM is storage that is quick and contrasts with long term storage on disk drives like the one in your computer or cloud storage on the Web. Before you can actually use the data it must move from long term storage to RAM. As a general rule, the best way to speed up your computer is to add more RAM up to the maximum RAM it can hold. Add RAM before updating anything else on your computer.
- record
- Structured information/data is usually organized in rows and columns. A well formed record contains a series of cells or "fields" of data, each holding one item (like a first name). All the fields for one person in a contact list are found in the same row or "record."
- right-click
- When you click the right mouse button, a context menu typically appears. Context menus reveal actions you may do that are specifically related to the object/icon you clicked.
- router
- Connecting to the Internet requires an extra piece of equipment. The router installed by your cable or phone company gives you the link from within your house to the wiring of the Internet. The connection links your computer to an electronic "internet protcol" or "IP" address. Lots of engineering went into the setup of the addresses, but your computer and the router handle it all for you automatically. Hook up the computer and router with the special cord and off you go.
- save/saving
- Any work you do in a computer is temporary, surviving only until a copy of the work is stored on long term storage. The computer has a disk drive on which you may save a copy of a document, photo, song, etc. If you don't save it, your work will be lost when you turn off your computer.
- scrolling
- Most often describes moving up or down a “page” that is longer than the visible screen. Most windows have a visible bar along the right edge. It is possible to move up and down (vertical scroll) through the document/page by clicking and dragging the scroll bar. Some windows also display a scroll bar at the bottom of the window allowing horizontal shifting/scrolling of the image.
- scroll wheel
- Some mice have a wheel between the two buttons. Using the wheel, you can scroll vertically without using the window scroll bar.
- social network
- The Internet was designed to be a way to share and to communicate. Social networking is one aspect of that, but didn't happen right at the start. At the dawn of the World Wide Web, a person needed to be a techie. Today, services like Twitter, Facebook, Google+, among others, provide a very easy way to share ones thoughts to a potentially huge audience. Social networking takes less effort than blogging, for example. Twitter is particularly notable for limiting each post to a maximum of 140 characters. Being consise has value in a "tweet."
- sorting
- Arranging information in order of number value or by alphabet is one of the powerful jobs that a computer does well. The technique is called "sorting" instead of "arranging." The sorting rule is strict, though. Sorting compares a list of data one character at a time. Every character counts, digits, spaces, punctuation and regular alphabetic letters.
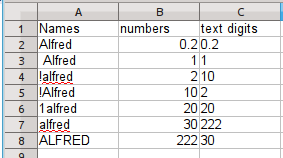 Numbers may be sorted as numbers, low value to high, but, looking carefully at the image to the left, you should note that sometimes numbers ARE NOT numbers. The digits can be treated like letters, as in column C. Note that when numbers are treated as letters, 2, 20 and 222 are in order, ignoring the numeric values. 10 is before 2 and 30 is after 222.
Numbers may be sorted as numbers, low value to high, but, looking carefully at the image to the left, you should note that sometimes numbers ARE NOT numbers. The digits can be treated like letters, as in column C. Note that when numbers are treated as letters, 2, 20 and 222 are in order, ignoring the numeric values. 10 is before 2 and 30 is after 222.
In column A, the order of the name is partially determined by the leading digits, the exclamation point, and the capitalization.
- SSD
- Solid State Drive - As of 2016, we are in a transition from the use of the older hard drives with their rotating disks holding the long term data in a computer, and are switching to drives which store data in much the same way as a USB thumb drive does. The data storage does not require that power be on in the computer.
- tap-to-click
- The laptop default setting for a touchpad is to allow you to tap the area of the touchpad as a substitute for a left-click of the left button below the touchpad.
- software
- Computers follow your directions, but you don't want to write every machine code. You need software to make your jobs easier to accomplish. Without software, your computer hardware is mainly a lump of plastic, metal and switches.
- SPAM
- Some messages you get through email are intended to fool or defraud you, trying to encourage you to do something which will give away important personal information. Most email systems work hard to automatically classify email so as to keep you from having dozens of such unwanted emails from reaching you every day. You need to help train your own email system to be sure you don't miss real emails and to give your email system the help to identify what is SPAM.
- terabyte
- (abbreviation: TB) As of 2016, long term storage is measured as in terabytes, 1000 times bigger than gigabytes. Gigabytes, during the same timeframe, are common for computer RAM sizes.
- terms of service (TOS)
- Internet services of all kinds have an agreement you acknowledge by using the service. This agreement is a contract which you don't even need to sign. Just by using the service, you agree to the terms, as written. The provider can change the terms without notice. Be sure you think before commiting to a service. Even if you don't read the TOS, understand that you may be giving others access to the work you generate or store on the service. If privacy is a concern to you, definitely read the TOS and discuss the implications of using the service with advisors and friends before you commit your work to the service.
- tool tip
- A modern graphical user interface (GUI) tries to tell you as much as it can to guide your actions. Hovering the mouse pointer over some parts of a program window, such as the icons of the toolbar will show a small text message to guide you in using the tool.
- touchpad
- A laptop can be used with a mouse, but typically has a rectangular area that is sensitive to touch. Moving a fingertip across the touchpad will move the mouse pointer in the direction you move your fingertip.
- tower
- A common form of the box in which the main electronics of the computer are found. A tower may actually be placed on a desk which leads to the the “desktop” term, but many people place the tower inside a desk enclosure or put it on the floor beside the desk. While many people refer to the visible computer box as the "CPU", try to avoid that. The CPU is a relatively small electronic component at the core of all the other parts of a computer. The small CPU is inside the tower, but so are many other important parts like the hard drive. It wouldn't make you sound tech-savvy to call the tower a "disk drive" either.
- username
- Every person gets a user account on a GNU/Linux computer unless they share someone else's account. Online sites may also have you create a username in combination with a secure password, too.
- WAN (wide area network)
- "Wide Area Network" is generally used as another term for "The Internet", though it might also refer to a private network connection between buildings of a large company.
- word processing
- One of the earliest uses of personal computers was to make writing and editing a document easier. Before "PC" computers, doing a revision meant writing the corrections onto a printed copy of the document. Then somebody typed the new version, from scratch. Word processing allows us to store electronic copies of each document so making changes only involves careful editing and then reprinting the document. Word processing handles all the issues like margins automatically, too. It is rare to see rooms full of secretaries typing all day long to do the required revisions. The smaller number of people are now often called administrative assistants instead of secretaries. As you might suspect, this document has been reworked many times to reflect the changing world of computers.
WWW (World Wide Web) Information accessed from the Internet which uses the HTML language to structure the look so that it is more pleasing and impressive than just simple text. Increasingly, web pages are created using more advanced languages like JavaScript, PHP, Python and others, with Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) used to enhance the layout and look of the pages.
© 2013- Algot Runeman - Shared using the Creative Commons Attribution license.
Source to cite: - filedate:


 to generate a new word pair. Official CAPTCHA Site
to generate a new word pair. Official CAPTCHA Site
 Numbers may be sorted as numbers, low value to high, but, looking carefully at the image to the left, you should note that sometimes numbers ARE NOT numbers. The digits can be treated like letters, as in column C. Note that when numbers are treated as letters, 2, 20 and 222 are in order, ignoring the numeric values. 10 is before 2 and 30 is after 222.
Numbers may be sorted as numbers, low value to high, but, looking carefully at the image to the left, you should note that sometimes numbers ARE NOT numbers. The digits can be treated like letters, as in column C. Note that when numbers are treated as letters, 2, 20 and 222 are in order, ignoring the numeric values. 10 is before 2 and 30 is after 222.